
Learn from your fellow PHP developers with our PHP blogs, or help share the knowledge you've gained by writing your own.

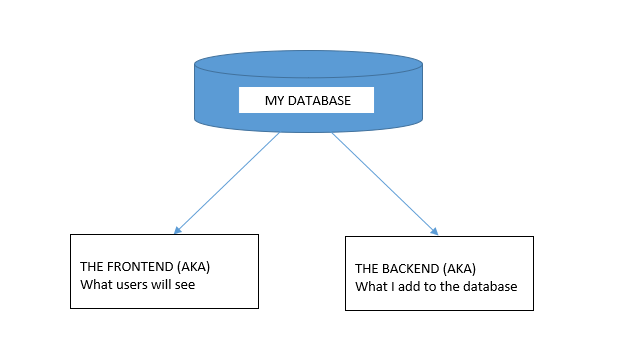
Your biggest asset is also your biggest risk... your developers

hasManyThrough() for the relation Schema::create('users', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->string('email')->unique();
$table->string('password');
$table->integer('country_id')->unsigned();
$table->rememberToken();
$table->timestamps();
$table->foreign('country_id')->references('id')->on('countries')
->onDelete('cascade');
});
Schema::create('posts', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string("name");
$table->integer('user_id')->unsigned();
$table->timestamps();
$table->foreign('user_id')->references('id')->on('users')
->onDelete('cascade');
});
Schema::create('countries', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->timestamps();
});
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Country extends Model
{
public function posts(){
return $this->hasManyThrough(
Post::class,
User::class,
'country_id',
'user_id',
'id',
'id'
);
}
}
$country = Country::find(1);
dd($country->posts);
morphMany() and morphTo() for relation.Schema::create('posts', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string("name");
$table->timestamps();
});
Schema::create('videos', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string("name");
$table->timestamps();
});
Schema::create('comments', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string("body");
$table->integer('commentable_id');
$table->string("commentable_type");
$table->timestamps();
});
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Post extends Model
{
public function comments(){
return $this->morphMany(Comment::class, 'commentable');
}
}
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Video extends Model{
public function comments(){
return $this->morphMany(Comment::class, 'commentable');
}
}
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Comment extends Model{
public function commentable(){
return $this->morphTo();
}
}
$post = Post::find(1);
$comment = new Comment;
$comment->body = "Hi Harikrishnan";
$post->comments()->save($comment);
$video = Video::find(1);
$comment = new Comment;
$comment->body = "Hi Harikrishnan";
$video->comments()->save($comment);
$post = Post::find(1);
dd($post->comments);
$video = Video::find(1);
dd($video->comments);
morphToMany() and morphedByMany() will be used for many to many polymorphic relationshipsSchema::create('posts', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string("name");
$table->timestamps();
});
Schema::create('videos', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string("name");
$table->timestamps();
});
Schema::create('tags', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string("name");
$table->timestamps();
});
Schema::create('taggables', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->integer("tag_id");
$table->integer("taggable_id");
$table->string("taggable_type");
});
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Post extends Model
{
public function tags(){
return $this->morphToMany(Tag::class, 'taggable');
}
}
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Video extends Model
{
public function tags(){
return $this->morphToMany(Tag::class, 'taggable');
}
}
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Tag extends Model
{
public function posts(){
return $this->morphedByMany(Post::class, 'taggable');
}
public function videos(){
return $this->morphedByMany(Video::class, 'taggable');
}
}
$post = Post::find(1);
$tag = new Tag;
$tag->name = "Hi Harikrishnan";
$post->tags()->save($tag);
$video = Video::find(1);
$tag = new Tag;
$tag->name = "Vishnu";
$video->tags()->save($tag);
$post = Post::find(1);
$tag1 = new Tag;
$tag1->name = "Kerala Blasters";
$tag2 = new Tag;
$tag2->name = "Manajapadda";
$post->tags()->saveMany([$tag1, $tag2]);
$video = Video::find(1);
$tag1 = new Tag;
$tag1->name = "Kerala Blasters";
$tag2 = new Tag;
$tag2->name = "Manajappada";
$video->tags()->saveMany([$tag1, $tag2]);
$post = Post::find(1);
$tag1 = Tag::find(3);
$tag2 = Tag::find(4);
$post->tags()->attach([$tag1->id, $tag2->id]);
$video = Video::find(1);
$tag1 = Tag::find(3);
$tag2 = Tag::find(4);
$video->tags()->attach([$tag1->id, $tag2->id]);
$post = Post::find(1);
$tag1 = Tag::find(3);
$tag2 = Tag::find(4);
$post->tags()->sync([$tag1->id, $tag2->id]);
$video = Video::find(1);
$tag1 = Tag::find(3);
$tag2 = Tag::find(4);
$video->tags()->sync([$tag1->id, $tag2->id]);
$post = Post::find(1);
dd($post->tags);
$video = Video::find(1);
dd($video->tags)
$tag = Tag::find(1);
dd($tag->posts);
$tag = Tag::find(1);
dd($tag->videos);
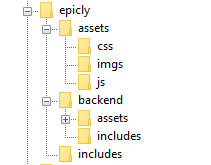
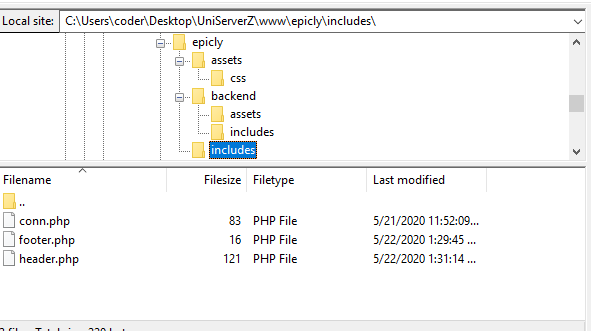
<html>
<head>
<title>My Awesome CMS – Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
</head> tag. <link href=”../assets/css/style.css” type=”text/css” rel=”stylesheet”/>
<?php tag. <div id="myfirstid"></div>
<div class="myfirstclass"></div>
<div class="myfirstclass"></div>
<div class="myfirstclass"></div>
<div class="myfirstclass"></div>
<div class="myfirstclass"></div>
#myfirstid{
Background:lightblue;
Font-family:Arial;
Font-size:44px;
Font-weight: Bold;
}
.myfirstclass{
Font-size:15px;
Color: darkblue;
}
include(‘includes/header.php’);
<divs> we used for practice earlier, we have something better in store! include(‘includes/footer.php’);
foreach($getmydata as $mydata){ echo "Title: "; echo $mydata['title']; echo "<br/>"; echo "Content: "; echo $mydata['content']; echo "<br/>"; echo "Author: "; echo $mydata['author']; echo "<br/>"; echo "<br/>";
?>
<div id=”myfirstid”>
<?php
foreach($getmydata as $mydata){
echo "<div class=”myfirstclass”>Title: ";
echo $mydata['title'];
echo "<br/>";
echo "Content: ";
echo $mydata['content'];
echo "<br/>";
echo "Author: ";
echo $mydata['author'];
echo "</div><br/><br/>";
}?>
</div>
<?php
<?php
include('includes/header.php');
include('includes/conn.php');
if ($letsconnect -> connect_errno) { echo "Error " . $letsconnect -> connect_error;
}else{
$getmydata=$letsconnect -> query("SELECT * FROM content");
?>
<div id="myfirstid">
<?php
foreach($getmydata as $mydata){
echo "<div class=”myfirstclass”>Title: ";
echo $mydata['title'];
echo "<br/>";
echo "Content: ";
echo $mydata['content'];
echo "<br/>";
echo "Author: ";
echo $mydata['author'];
echo "</div><br/><br/>";
}
?>
</div>
<?php
}
$letsconnect -> close();
include('includes/footer.php');
?>
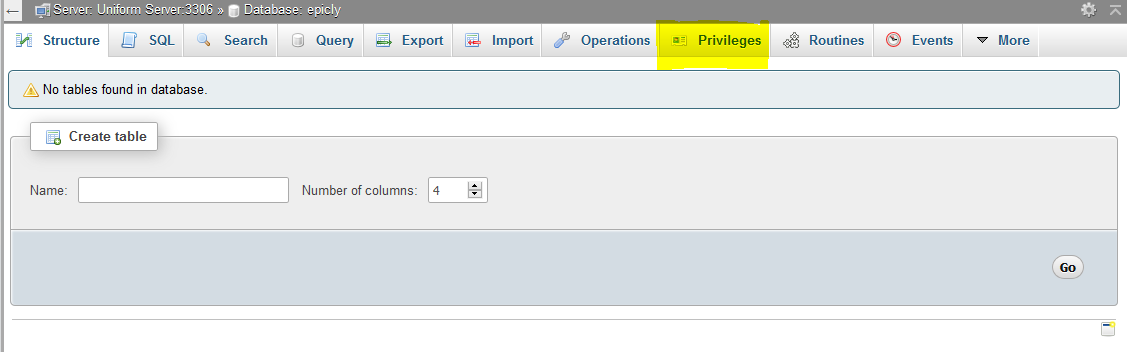
CREATE TABLE <code>mydbname</code>.<code>content</code> ( <code>ID</code> INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT , <code>title</code> VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL , <code>content</code> LONGTEXT NOT NULL , <code>author</code> VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (<code>ID</code>)) ENGINE = MyISAM COMMENT = 'content table';
conn.php file in your root/includes folder.conn.php file, remember to include your own database credentials.
<?php
$letsconnect = new mysqli("localhost","dbuser","dbpass","dbname");
?>
index.php at the root of your CMS folder.
<?php
include('includes/conn.php');
if ($letsconnect -> connect_errno) { echo "Error " . $letsconnect -> connect_error;
}else{
$getmydata=$letsconnect -> query("SELECT * FROM content");
foreach($getmydata as $mydata){ echo "Title: "; echo $mydata['title']; echo "<br/>"; echo "Content: "; echo $mydata['content']; echo "<br/>"; echo "Author: "; echo $mydata['author']; echo "<br/>"; echo "<br/>";
}
}
$letsconnect -> close();
?>
index.php in your backend folder.
<html>
<head><title>Backend - Capture Content</title></head>
<body>
<form action="<?php $_SERVER[‘PHP_SELF’];?>" method="post">
<input type="text" name="title" placeholder="Content Title here" required/>
<textarea name="content">Content Here</textarea>
<input type="text" name="author" placeholder="Author" required/>
<input type="submit" value="Save My Data" name="savedata"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
<form>
<?php
if(isset($_POST['savedata'])){
include('../includes/conn.php');
if ($letsconnect->connect_error) {
die("Your Connection failed: " . $letsconnect->connect_error);
}else{
$sql = "INSERT INTO content(title,content,author)VALUES ('".$_POST["title"]."', '".$_POST["content"]."', '".$_POST["author"]."')";
if (mysqli_query($letsconnect, $sql)) {
echo "Your data was saved successfully!";
} else { echo "Error: " . $sql . "" . mysqli_error($letsconnect);
} $letsconnect->close();
}
}
?>
Note, this is a basic MySQL query to insert data. However, before using this in production it's important to add proper escaping and security to prevent SQL injections. This will be covered in the next article.



 g10dra
g10dra crocodile2u
crocodile2u calevans
calevans christiemarie
christiemarie dmamontov
dmamontov HowTos
HowTos tanja
tanja
