
Learn from your fellow PHP developers with our PHP blogs, or help share the knowledge you've gained by writing your own.

umask(0);
$pid = pcntl_fork();
if ($pid < 0) {
print('fork failed');
exit 1;
}
if ($pid > 0) { echo "daemon process started
";
exit;
}
$sid = posix_setsid();
if ($sid < 0) {
exit 2;
}
chdir('/');
file_put_contents($pidFilename, getmypid() );
run_process();ob_start();
var_dump($some_object);
$content = ob_get_clean();
fwrite($fd_log, $content); ini_set('error_log', $logDir.'/error.log');
fclose(STDIN);
fclose(STDOUT);
fclose(STDERR);
$STDIN = fopen('/dev/null', 'r');
$STDOUT = fopen($logDir.'/application.log', 'ab');
$STDERR = fopen($logDir.'/application.error.log', 'ab');
function sig_handler($signo)
{
global $fd_log;
switch ($signo) {
case SIGTERM:
fclose($fd_log); unlink($pidfile); exit;
break;
case SIGHUP:
init_data(); break;
default:
}
}
pcntl_signal(SIGTERM, "sig_handler");
pcntl_signal(SIGHUP, "sig_handler");
$base = event_base_new();
$event = event_new();
$errno = 0;
$errstr = '';
$socket = stream_socket_server("tcp://$IP:$port", $errno, $errstr);
stream_set_blocking($socket, 0);
event_set($event, $socket, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, 'onAccept', $base);
function onRead($buffer, $id)
{
while($read = event_buffer_read($buffer, 256)) {
var_dump($read);
}
}
function onError($buffer, $error, $id)
{
global $id, $buffers, $ctx_connections;
event_buffer_disable($buffers[$id], EV_READ | EV_WRITE);
event_buffer_free($buffers[$id]);
fclose($ctx_connections[$id]);
unset($buffers[$id], $ctx_connections[$id]);
}
$event2 = event_new();
$tmpfile = tmpfile();
event_set($event2, $tmpfile, 0, 'onTimer', $interval);
$res = event_base_set($event2, $base);
event_add($event2, 1000000 * $interval);
function onTimer($tmpfile, $flag, $interval)
{
$global $base, $event2;
if ($event2) {
event_delete($event2);
event_free($event2);
}
call_user_function(‘process_data’,$args);
$event2 = event_new();
event_set($event2, $tmpfile, 0, 'onTimer', $interval);
$res = event_base_set($event2, $base);
event_add($event2, 1000000 * $interval);
}
event_delete($event);
event_free($event);
event_base_free($base);
event_base_set($event, $base);
event_add($event);
function onAccept($socket, $flag, $base) {
global $id, $buffers, $ctx_connections;
$id++;
$connection = stream_socket_accept($socket);
stream_set_blocking($connection, 0);
$buffer = event_buffer_new($connection, 'onRead', NULL, 'onError', $id);
event_buffer_base_set($buffer, $base);
event_buffer_timeout_set($buffer, 30, 30);
event_buffer_watermark_set($buffer, EV_READ, 0, 0xffffff); event_buffer_priority_set($buffer, 10); event_buffer_enable($buffer, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST); $ctx_connections[$id] = $connection;
$buffers[$id] = $buffer;
}
#! /bin/sh
#
$appdir = /usr/share/myapp/app.php
$parms = --master –proc=8 --daemon
export $appdir
export $parms
if [ ! -x appdir ]; then
exit 1
fi
if [ -x /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions ]; then
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
fi
RETVAL=0
start () {
echo "Starting app"
daemon /usr/bin/php $appdir $parms
RETVAL=$?
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && touch /var/lock/subsys/mydaemon
echo
return $RETVAL
}
stop () {
echo -n "Stopping $prog: "
killproc /usr/bin/fetchmail
RETVAL=$?
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && rm -f /var/lock/subsys/mydaemon
echo
return $RETVAL
}
case in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart)
stop
start
;;
status)
status /usr/bin/mydaemon
;;
*)
echo "Usage: {start|stop|restart|status}"
;;
RETVAL=$?
exit $RETVAL
#php app.phar
myDaemon version 0.1 Debug
usage:
--daemon – run as daemon
--debug – run in debug mode
--settings – print settings
--nofork – not run child processes
--check – check dependency modules
--master – run as master
--proc=[8] – run child processes
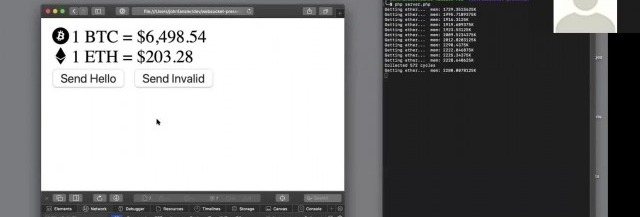
WebSockets have compatibility with 96.5% of clients globally
OnConnection method.OnOpen gets called when a new connection is made.OnClose gets called when a client quits. It's essential to keep an eye on memory management, and essential to keep tidying up as you move through the code.OnError gets called when there is an exception faced by the user.OnMessage gives the text of the JSON message, which is being exchanged with the client.
var_dump(), which is obviously not the best way to do it. If you see the code for the first time, if you work with legacy code - step-by-step interactive debugging is the way to go. Sometimes it can save you hours of old school var_dumping.watch phpunit /path/to/test while developing: this way the test is run every 2 seconds, you switch to the terminal whenever you want to see the latest results and that's it. However, there are certain advantages in running tests from the IDE. First, it's super-handy to launch a test method, test class or a whole folder with tests, just by pressing a hotkey. Second, the test results appear right there, in PHPStorm, with failures and their stack traces, every entry clickable and takes you directly to the file:line where a nasty thing happened. I also find the ability to run a debugger for a unit test, extremely attractive. Test fails, you click on a trace entry, get to a problematic line, place a break point, re-run the test in debug mode - and there you go.$HOME/projects/cool-project, but inside a docker or on a remote host it might be located at /app or /var/www, then you have to let PHPStorm know about this.Debugging is like being the detective in a crime movie where you are also the murderer. Filipe Fortes a.k.a. @fortes

$cache = app("cache");
app("cache"") and expect a Cache\Repository instance as result. If I pass the result of this call to a function that requires a Cache\Repository as parameter, I will probably have a code inspection warning from IDE. Moreover, if I want proper autocompletion, I will have to add additional comment:
$cache = app("cache");
namespace App;
class MyApp extends Application
{
public function cacheRepository(): Repository
{
return $this->make(Repository::class);
}
}
TypeError in case of a misconfiguration, and I have a type-hint which allows the IDE to recognize the return value. Bye-bye nasty comment lines and IDE warnings! I make a method per service, with type-hints, like dbConnection() or viewFactory() - works really well for me!bootstrap/app.php, should reside in that custom class:namespace App;
class MyApp extends Application
{
public function __construct()
{
define('LARAVEL_START', microtime(true));
define("APP_ROOT", realpath(__DIR__ . "/../"));
parent::__construct(APP_ROOT);
$this->setUp();
}
private function setUp()
{
$this->singleton(
Contracts\Http\Kernel::class,
\App\Http\Kernel::class
);
}
}
bootstrap/app.php becomes just this:return new \App\MyApp;
app() function will also return an instance of MyApp from now on. However, it's @phpdoc says it returns \Illuminate\Foundation\Application, so for better clarity, I also added my own accessor method:namespace App;
class MyApp extends Application
{
public static function app(): self
{
$ret = parent::getInstance();
return $ret;
}
}
MyApp::app(). The IDE wil be aware of the return type due to the type-hint, so I get everything I want for clean and clear development.



 g10dra
g10dra harikrishnanr
harikrishnanr calevans
calevans MindNovae
MindNovae tanja
tanja damnjan
damnjan ahmedkhan
ahmedkhan
